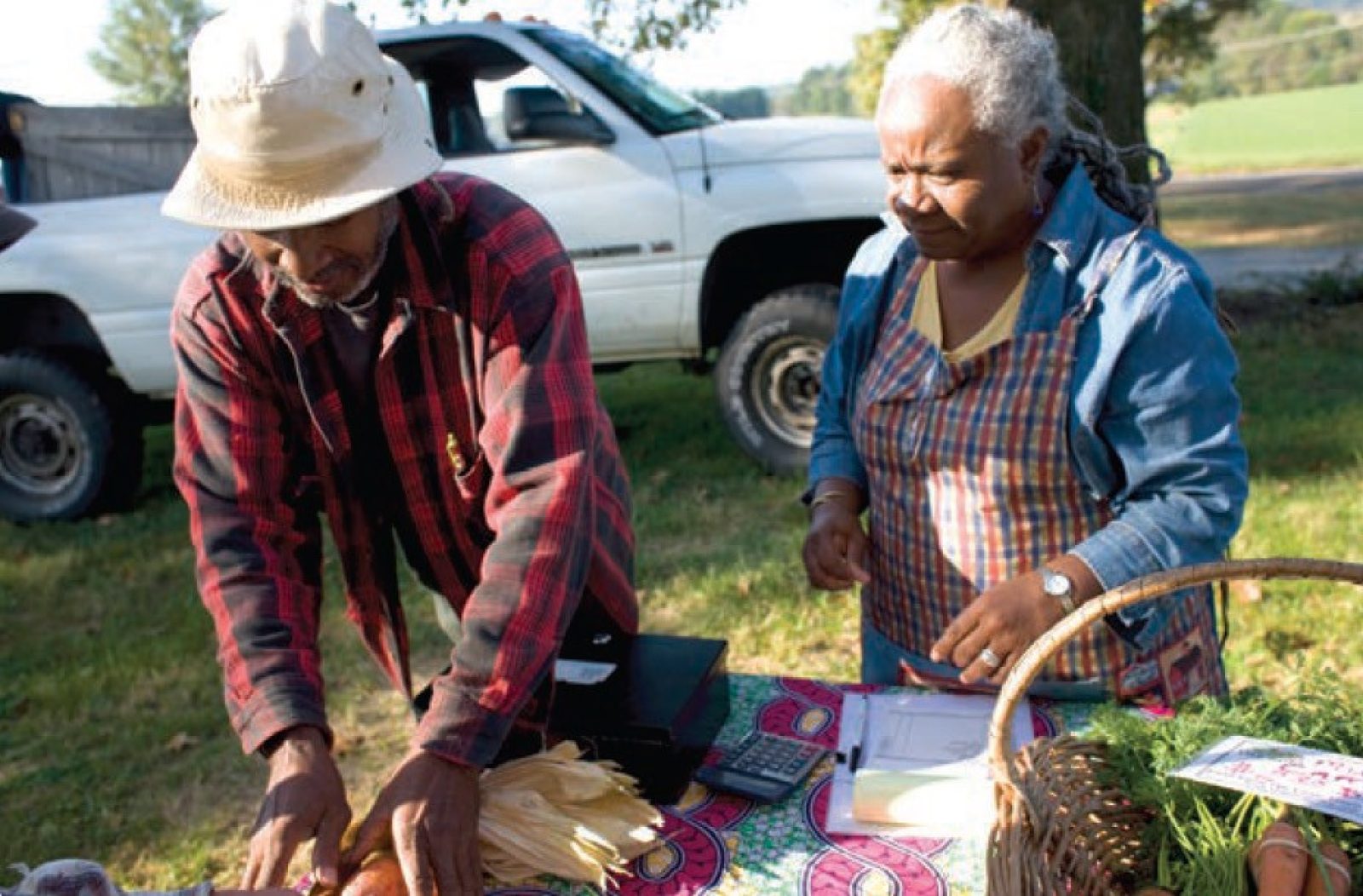
Sustainable Agriculture
Lesson Plans & Online Learning

Featured!

Food and Farm Facts
In The Boat e-Learning Module
Up-close Experience: Combines

Pork Ag Mag
On the Christmas Tree Farm e-Learning Module

Sustainable Agriculture














